How safe are mass construction projects?

Radon (radonum) is a chemical radioactive element belonging to the VIII group of the periodic system of Mendeleev. It refers to inert gases. This isotope was discovered by the German scientist radon Dorn in 1899. Currently, more than 20 isotopes of radon are known. 3 isotopes of radon are included in the offer of isotopes in the natural 3rd radioactive series. They are found in air, water and soil.
Due to its gaseous state, radon spreads through the pores and cracks of the earth's rocks. It exits (is released) from the earth into the atmosphere, water, and then into the air of the building. The main sources of radon in the building air are the underground soils of the building, its release from building materials and structures.
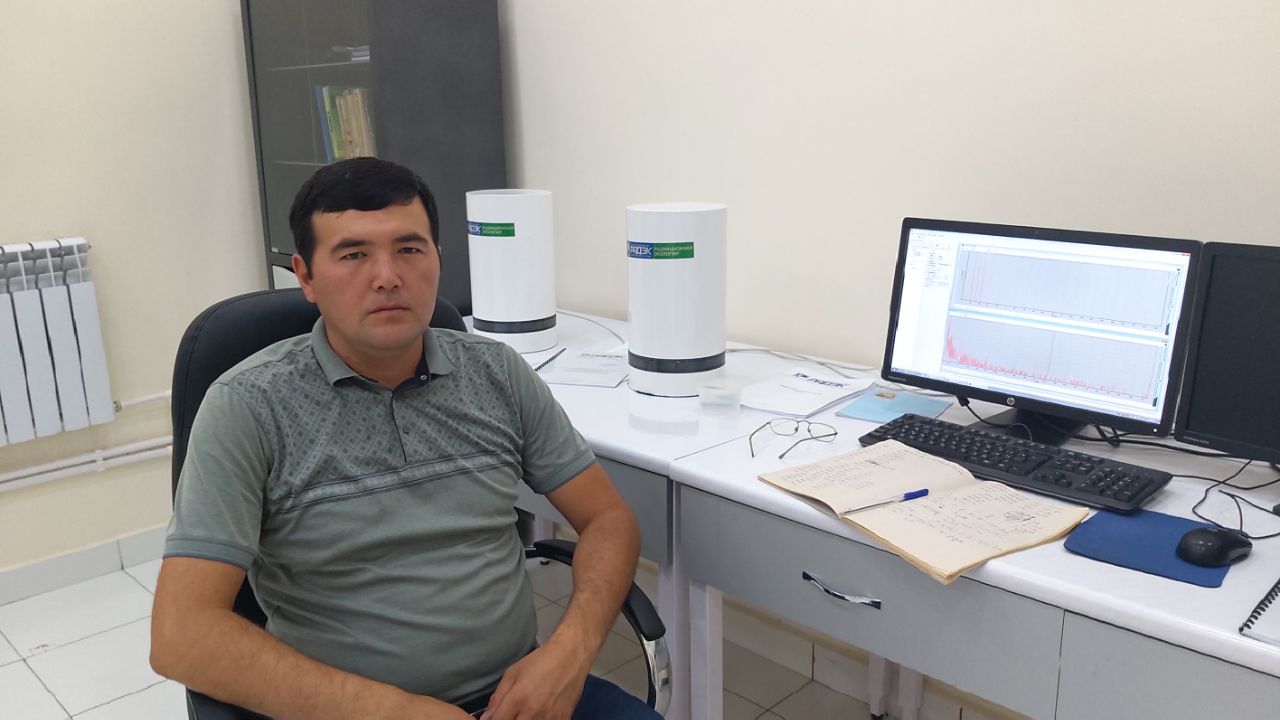
Doctoral student of the Department of Nuclear Physics and Astronomy of the Faculty of Physics of Samarkand State University Eldor Umrzakov conducts research work on the topic "Assessment of the potential radon hazard of mass construction facilities in rural areas of Uzbekistan." To date, the scientist's articles and abstracts have been published in more than 30 international and national publications. Scientific supervisor Doctor of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Professor Kholbaev Isobek.
- Another source of radon entering the building is natural water, - says Eldar Umrzakov. - When using domestic or industrial, i.e. process water in premises, radon flies out of it and mixes with the air in the building, thereby adding its share of the total radiation hazard when radon is absorbed in the air of the building by breathing.
To determine the average annual effective dose, the following radiation factors are estimated, which contribute the main share to it:
Equivalent dose rate of gamma radiation
Average annual volumetric activity pH-222 in building air
Density of radon flux on the soil surface
Volumetric activity of radon in drinking water
Comparative total alpha and beta activity in drinking water
The effective activity of natural radionuclides along with radon during the construction of new residential, public and industrial facilities is observed in building materials, as well as in soils used for pumping soils displaced during construction and landscaping.
The average annual effective radiation volumetric activity of elements resulting from the decay of radon in the air of residential premises of operated buildings should not exceed 400 Bq/m3. At high activity values, protective measures should be taken to reduce the entry of radon into the room and improve its ventilation.
For the construction of industrial buildings, one should choose a site on the soil surface with a radon flux density of not more than 250 MBK/(m2s). If a building is designed with a radon flux density of more than 250 MBq/(m2s), then it is necessary to introduce a radon protection system.
In research work, he took part in expeditions to assess the radiation monitoring of new buildings, industrial enterprises and new deposits of natural resources, which are being built to this day in various regions of the republic, based on the results obtained, he monitored the site under study. In addition, he takes part in monitoring the radiation background at the construction site of the first nuclear power plant (NPP) in the republic, which is planned for construction, namely in the Farish district of the Jizzakh region. This is of great importance for assessing the impact of natural and man-made radionuclides in the future.

Information Service
Samarkand State University.