Have you ever heard of the leontitsa plant?
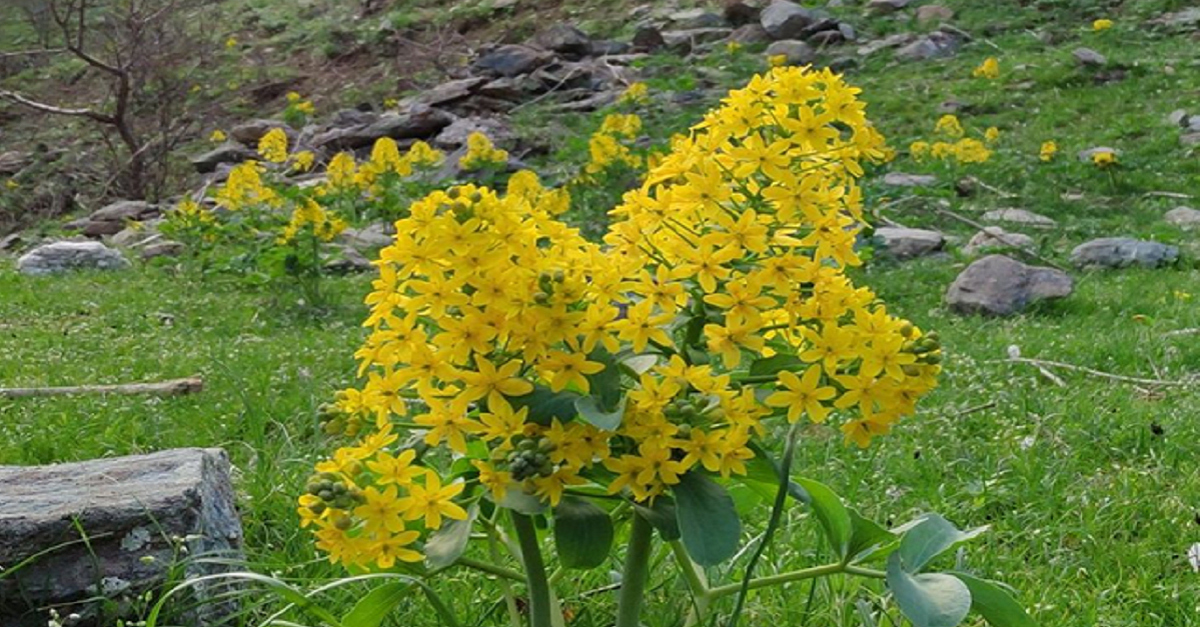

The green flora of Uzbekistan is incredibly rich and diverse. In addition to the medicinal plants you-he-know, we still find in the world of science the "rare wonders of nature" that it now brings. Leontitsa is one of these plants.
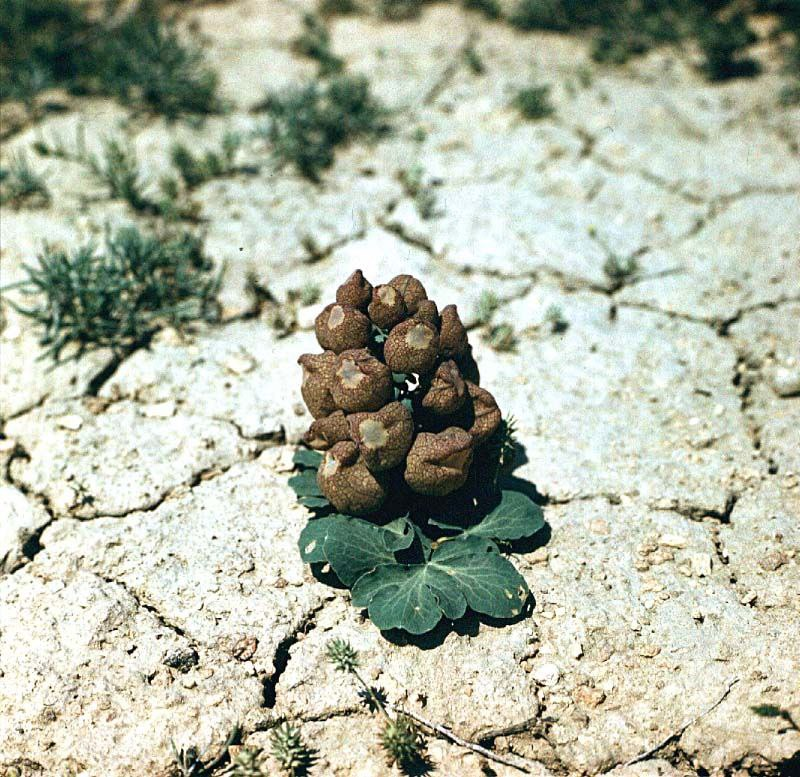
Leontitsa is a perennial plant growing on mountain slopes. An interesting phenomenon is connected with its name. The same ripe melon fruits, when mixed with water, form a kind of foam. According to reports, in ancient times, residents used leontitsa as soap.
A number of studies are being carried out at the Faculty of Biology of Samarkand State University to determine the bioecological properties of this plant. In particular, 1st-year masters Gulkhaya Gofurova and Iroda Saidullayeva, under the supervision of Associate Professor of the Department of Botany Zebunniso Nomozova, conduct scientific research on the chemical composition, growth conditions and characteristics of the leontitsa plant.
The birthplace of the leontitsa is Central Asia, it grows on loamy, clay soils, among non-irrigated crops, says Gulkhaya Gofurova. - Propagated by seeds and stem cuttings. The rhizome can be propagated in pieces. It is advisable to multiply by equal halves or by three. Blooms from mid-April, about 15 days. It is mainly adapted to growing on mountain slopes, in loamy, gravelly places.
The stem of the leontitsa is up to 1.2 cm high, thick, without hairs, blue-violet on the outside, elliptical or ovoid, longer than the petals, says Iroda Saydullaeva. - Burdock root, which accounts for 1-4 kg of ground soap, is very rich in saponin. Therefore, when mixing its fruits with water, a large amount of foam is formed. Due to this property, people used it as soap in ancient times.
Yersovun has been used in folk medicine since ancient times. It is used in medicine to treat diseases of the stomach. The rhizome contains up to 30% saponin, as well as terterpenes, glucose, arabinose, rhamnose, pahikarpin, etc. In Central Asian modern folk medicine, a decoction of its root was used to treat stomach ulcers, inflammation of the stomach, pulmonary tuberculosis, and blood diseases.


Iroda Bekmurodova
Information officer.
Samarkand State University
Photos taken by Shavkat Akramov.